Pyramid Of Pain [ 1 - 4 ]
1
Learn what is the Pyramid of Pain and how to utilize this model to determine the level of difficulty it will cause for an adversary to change the indicators associated with them, and their campaign.
This well-renowned concept is being applied to cybersecurity solutions like Cisco Security, SentinelOne, and SOCRadar to improve the effectiveness of CTI (Cyber Threat Intelligence), threat hunting, and incident response exercises.
Understanding the Pyramid of Pain concept as a Threat Hunter, Incident Responder, or SOC Analyst is important.
Are you ready to explore what hides inside the Pyramid of Pain?
2
As per Microsoft, the hash value is a numeric value of a fixed length that uniquely identifies data. A hash value is the result of a hashing algorithm. The following are some of the most common hashing algorithms:
- MD5 (Message Digest, defined by RFC 1321) - was designed by Ron Rivest in 1992 and is a widely used cryptographic hash function with a 128-bit hash value. MD5 hashes are NOT considered cryptographically secure. In 2011, the IETF published RFC 6151, "Updated Security Considerations for the MD5 Message-Digest and the HMAC-MD5 Algorithms," which mentioned a number of attacks against MD5 hashes, including the hash collision.
- SHA-1 (Secure Hash Algorithm 1, defined by RFC 3174) - was invented by United States National Security Agency in 1995. When data is fed to SHA-1 Hashing Algorithm, SHA-1 takes an input and produces a 160-bit hash value string as a 40 digit hexadecimal number. NIST deprecated the use of SHA-1 in 2011 and banned its use for digital signatures at the end of 2013 based on it being susceptible to brute-force attacks. Instead, NIST recommends migrating from SHA-1 to stronger hash algorithms in the SHA-2 and SHA-3 families.
- The SHA-2 (Secure Hash Algorithm 2) - SHA-2 Hashing Algorithm was designed by The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the National Security Agency (NSA) in 2001 to replace SHA-1. SHA-2 has many variants, and arguably the most common is SHA-256. The SHA-256 algorithm returns a hash value of 256-bits as a 64 digit hexadecimal number.
A hash is not considered to be cryptographically secure if two files have the same hash value or digest.
Security professionals usually use the hash values to gain insight into a specific malware sample, a malicious or a suspicious file, and as a way to uniquely identify and reference the malicious artifact.
You've probably read ransomware reports in the past, where security researchers would provide the hashes related to the malicious or suspicious files used at the end of the report. You can check out The DFIR Report and FireEye Threat Research Blogs if you’re interested in seeing an example.
Various online tools can be used to do hash lookups like VirusTotal and Metadefender Cloud - OPSWAT.
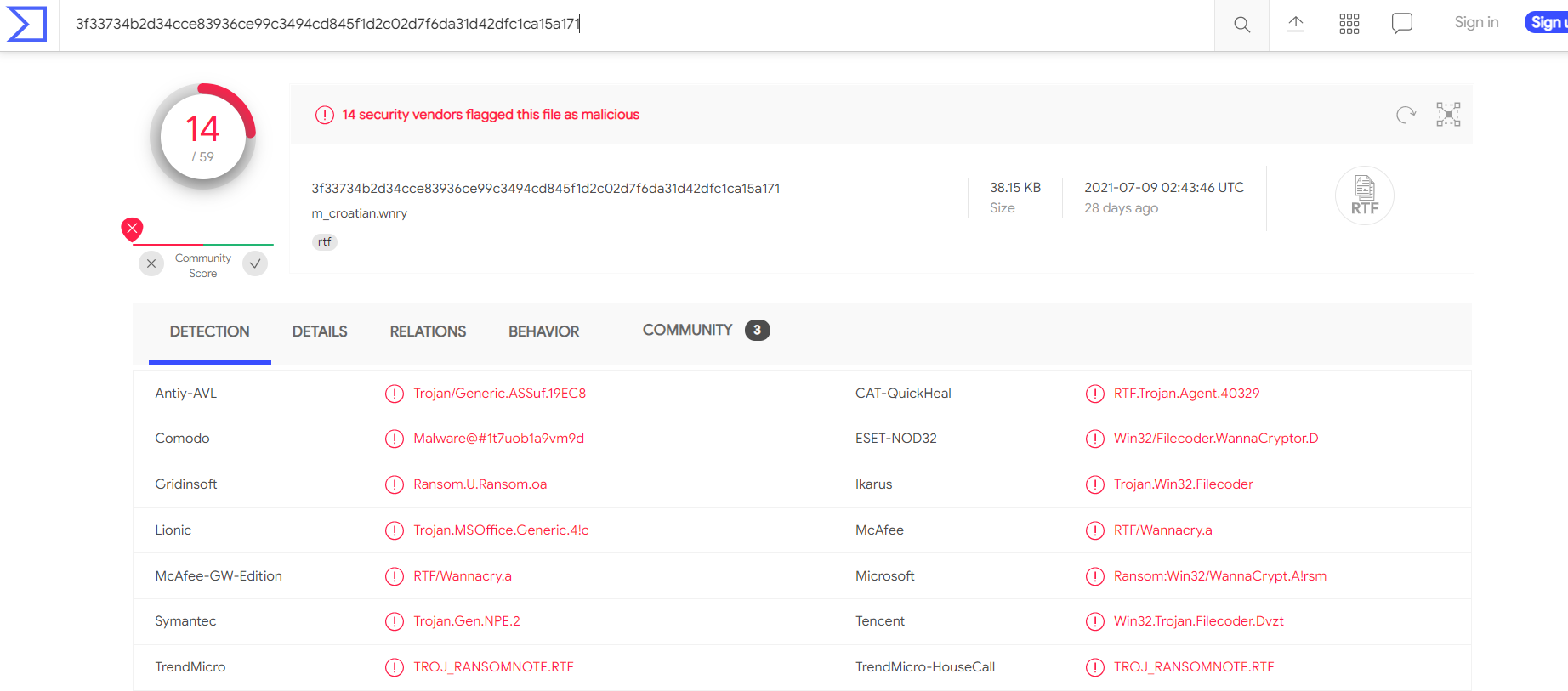
Below the hash in the screenshot above, you can see the filename. In this case, it is "m_croetian.wnry"
MetaDefender Cloud - OPSWAT:

As you might have noticed, it is really easy to spot a malicious file if we have the hash in our arsenal. However, as an attacker, modifying a file by even a single bit is trivial, which would produce a different hash value. With so many variations and instances of known malware or ransomware, threat hunting using file hashes as the IOC (Indicators of Compromise) can become difficult.
Let’s take a look at an example of how you can change the hash value of a file by simply appending a string to the end of a file using echo: File Hash (Before Modification)
PS C:\Users\THM\Downloads> Get-FileHash .\OpenVPN_2.5.1_I601_amd64.msi -Algorithm MD5
Algorithm Hash Path
_________ ____ ____
MD5 D1A008E3A606F24590A02B853E955CF7 C:\Users\THM\Downloads\OpenVPN_2.5.1_I601_amd64.msi
PS C:\Users\THM\Downloads> echo "AppendTheHash" >> .\OpenVPN_2.5.1_I601_amd64.msi
PS C:\Users\THM\Downloads> Get-FileHash .\OpenVPN_2.5.1_I601_amd64.msi -Algorithm MD5
Algorithm Hash Path
_________ ____ ____
MD5 9D52B46F5DE41B73418F8E0DACEC5E9F C:\Users\THM\Downloads\OpenVPN_2.5.1_I601_amd64.msi
3
You may have learned the importance of an IP Address from the "What is Networking?" Room. the importance of the IP Address. An IP address is used to identify any device connected to a network. These devices range from desktops, to servers and even CCTV cameras! We rely on IP addresses to send and receive the information over the network. But we are not going to get into the structure and functionality of the IP address. As a part of the Pyramid of Pain, we’ll evaluate how IP addresses are used as an indicator.
In the Pyramid of Pain, IP addresses are indicated with the color green. You might be asking why and what you can associate the green colour with?
From a defense standpoint, knowledge of the IP addresses an adversary uses can be valuable. A common defense tactic is to block, drop, or deny inbound requests from IP addresses on your parameter or external firewall. This tactic is often not bulletproof as it’s trivial for an experienced adversary to recover simply by using a new public IP address.
Malicious IP connections (app.any.run):

NOTE! Do not attempt to interact with the IP addresses shown above.
One of the ways an adversary can make it challenging to successfully carry out IP blocking is by using Fast Flux.
According to Akamai, Fast Flux is a DNS technique used by botnets to hide phishing, web proxying, malware delivery, and malware communication activities behind compromised hosts acting as proxies. The purpose of using the Fast Flux network is to make the communication between malware and its command and control server (C&C) challenging to be discovered by security professionals.
So, the primary concept of a Fast Flux network is having multiple IP addresses associated with a domain name, which is constantly changing. Palo Alto created a great fictional scenario to explain Fast Flux: "Fast Flux 101: How Cybercriminals Improve the Resilience of Their Infrastructure to Evade Detection and Law Enforcement Takedowns"
Read the following report (generated from any.run) for this sample here to answer the questions below:
4
Let's step up the Pyramid of Pain and move on to Domain Names. You can see the transition of colors - from green to teal.
Domain Names can be thought as simply mapping an IP address to a string of text. A domain name can contain a domain and a top-level domain (evilcorp.com) or a sub-domain followed by a domain and top-level domain (tryhackme.evilcorp.com). But we will not go into the details of how the Domain Name System (DNS) works. You can learn more about DNS in this "DNS in Detail" Room.
Domain Names can be a little more of a pain for the attacker to change as they would most likely need to purchase the domain, register it and modify DNS records. Unfortunately for defenders, many DNS providers have loose standards and provide APIs to make it even easier for the attacker to change the domain.
Malicious Sodinokibi C2 (Command and Control Infrastructure) domains:


Can you spot anything malicious in the above screenshot? Now, compare it to the legitimate website view below:

This is one of the examples of a Punycode attack used by the attackers to redirect users to a malicious domain that seems legitimate at first glance.
What is Punycode? As per Wandera, "Punycode is a way of converting words that cannot be written in ASCII, into a Unicode ASCII encoding."
What you saw in the URL above is adıdas.de which has the Punycode of http://xn--addas-o4a.de/
- bit.ly
- goo.gl
- ow.ly
- s.id
- smarturl.it
- tiny.pl
- tinyurl.com
- x.co

Viewing Connections in Any.run:
Because Any.run is a sandboxing service that executes the sample, we can review any connections such as HTTP requests, DNS requests or processes communicating with an IP address. To do so, we can look at the "networking" tab located just below the snapshot of the machine.
Please note: you should be extremely cautious about visiting any of the IP addresses or HTTP requests made in a report. After all, these are behaviours from the malware sample - so they're probably doing something dangerous!
HTTP Requests:
This tab shows the recorded HTTP requests since the detonation of the sample. This can be useful to see what resources are being retrieved from a webserver, such as a dropper or a callback.

Connections:
This tab shows any communications made since the detonation of the sample. This can be useful to see if a process communicates with another host. For example, this could be C2 traffic, uploading/downloading files over FTP, etc.

DNS Requests:
This tab shows the DNS requests made since the detonation of the sample. Malware often makes DNS requests to check for internet connectivity (I.e. if It can't reach the internet/call home, then it's probably being sandboxed or is useless).

What term refers to an address used to access websites?
What type of attack uses Unicode characters in the domain name to imitate the a known domain?
